有時候我們會需要用到 C# 的前置處理器指示詞(Preprocessor Directives) 中的 #if 等相關指示詞, 最常見的就是用來區分 Debug 和 Release 的編譯模式.
也有另外一種方式 (ConditionalAttribute) 可以達到類似的效果, 但兩種方式的運作機制是不一樣的.
這類型的條件編譯最常用在環境區分, 而不管用 #if 還是 ConditionalAttribute, 都要定義專案在各種模式下的 compilation symbol, 要注意的是這部分是大小寫敏感, 雖然用小寫不會有問題, 但一般來說是用全大寫, 例如: DEBUG.
設定方式如下: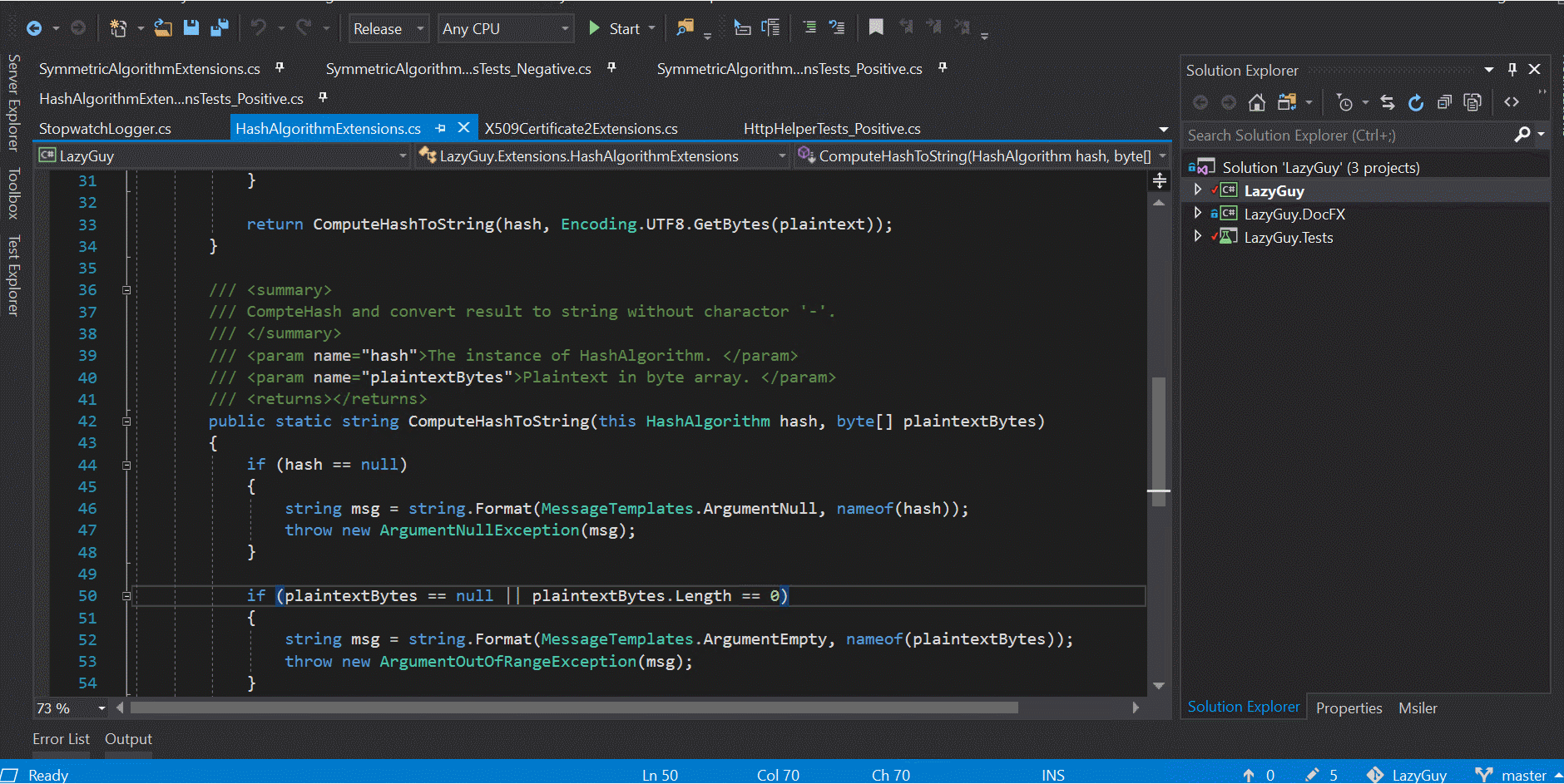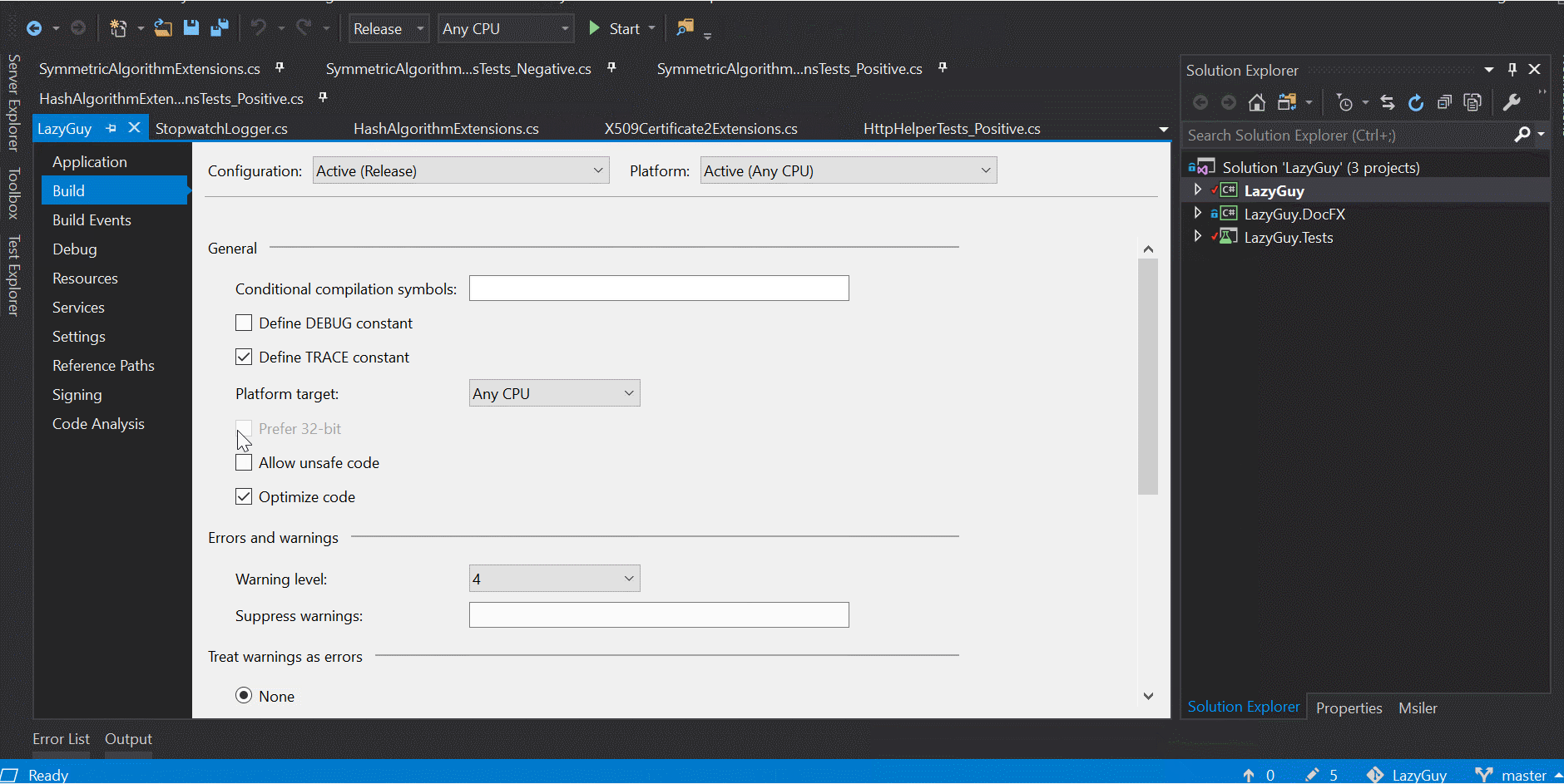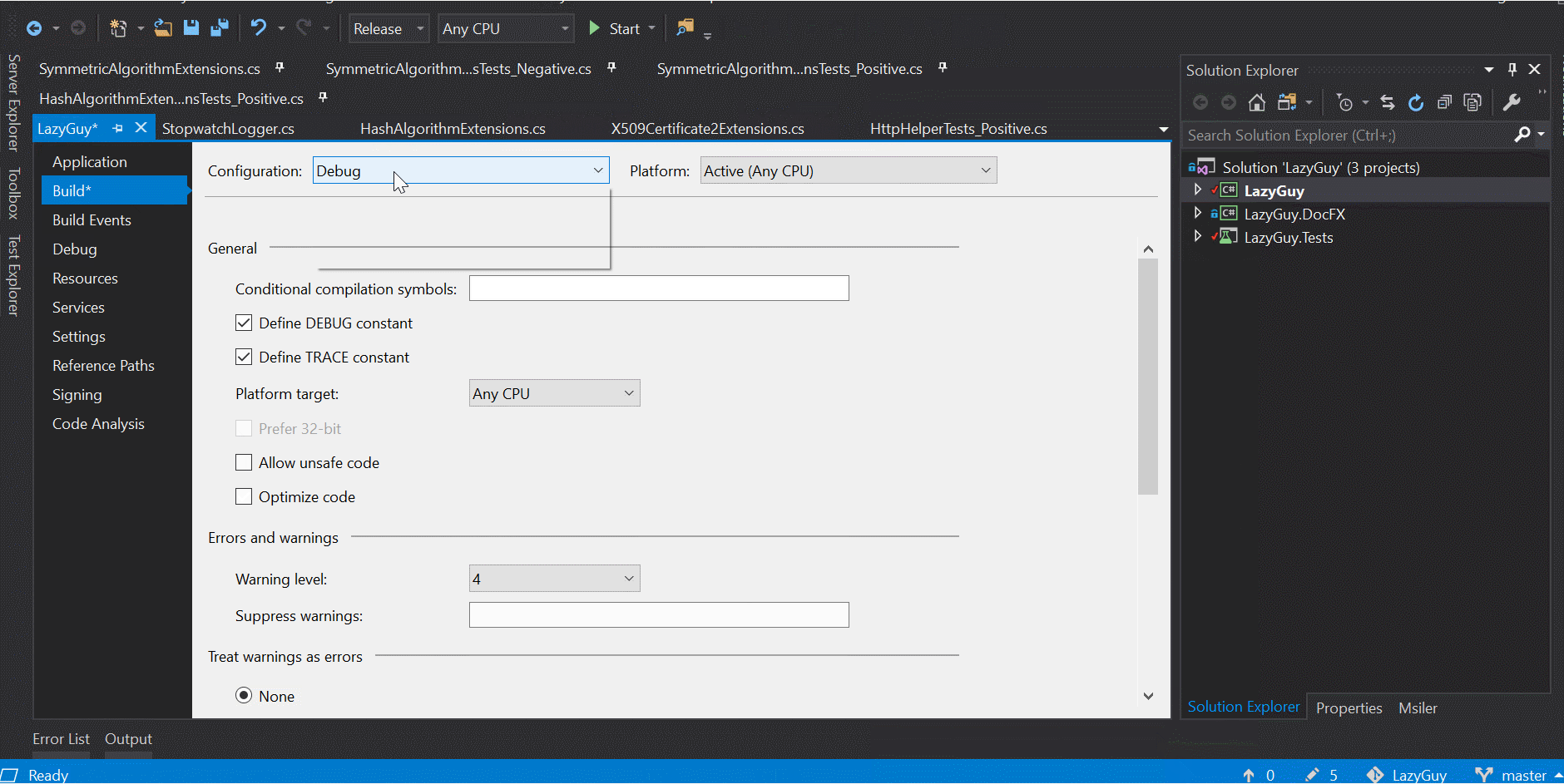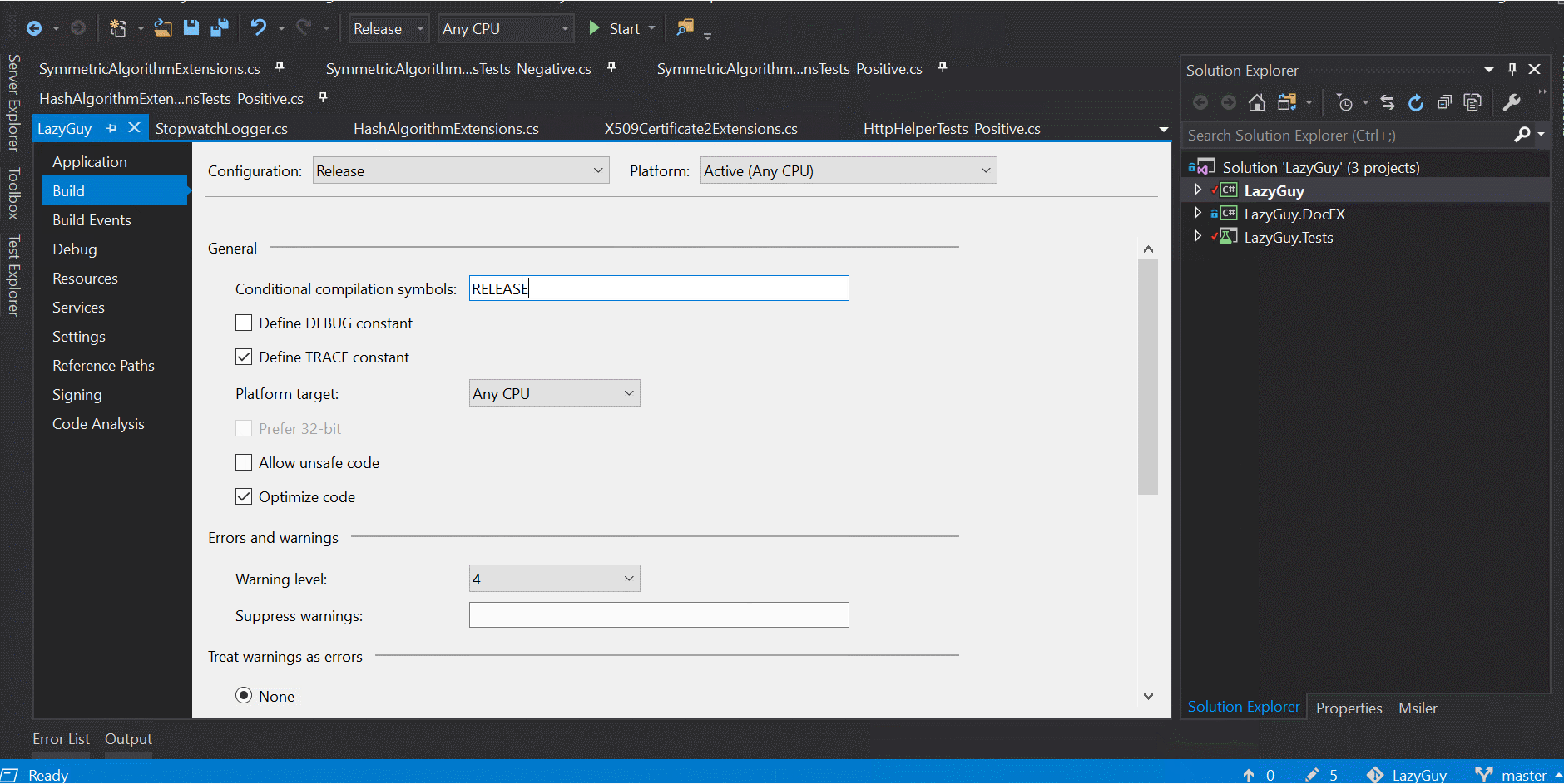
#if, #elif, #else
運作方式
被 #if, #elif 包起來的區間不符合定義的 compilation symbol 時, 編譯時會直接略過區間內的程式碼, 也就是說不會被編譯, 以下面程式碼與 IL 為例
1 | public void Caller() |
1 | IL_0000 nop |
透過工具, 我們可以看到在 DEBUG 下編譯, 只剩 DEBUG 區塊的程式碼.
優缺點
這樣雖然不需要的程式碼不會被編譯, 但是從使用方式看來, 如果不小心使用的話很容易讓程式碼變得很髒亂, 到處都是 #if, #elif 和 #else.
而從另外一個角度看, 因為不滿足條件的區塊不會被編譯, 所以很多 visual studio 提供的功能都會無法使用, 維護上很容易造成困擾, 例如在 DEBUG 下將一個方法重新命名, 結果這個方法在 RELEASE 區間有被呼叫到, 卻不會被修改到, 當切換到 RELEASE 的時候就無法通過編譯, 又例如尋找所有引用 (Find All References) 的功能也是一樣.
ConditionalAttribute
運作方式
當不符合 ConditionalAttribute 所套用的 compilation symbol 時, 編譯後會忽略呼叫端的呼叫, 但是保留被呼叫部分的程式碼, 以下面程式碼與 IL 為例
1 | public void Caller() |
1 | // Selected method: LazyGuy.Demo.Caller |
透過工具, 我們可以看到在 DEBUG 下編譯, 呼叫端的呼叫只剩 DebugConditional(), 而 RELEASEConditional() 這個方法還是會被編譯, 只是沒被呼叫.
優缺點
ConditionalAttribute 有很多使用限制
- 只能加在 void method 以及 attribute class 上
- 不能加在實作介面的方法上
- 不能加在 override 方法上
這個方法雖然限制很多, 但是也有很多好處如下:
首先, 因為 ConditionalAttribute 只能加在 void method 以及 attribute class 上, 所以變相強制我們將這些程式碼抽出成獨立的方法, 避免 #if 會產生的副作用.
即使將 #if 中的程式碼抽出成獨立方法, 但因為編譯時並不會移除呼叫端的呼叫, 所以會變成呼叫一個空方法, 也不是太好, 反之 ConditionalAttribute 就不會有這個問題.
第二, 他也不會有 #if 在使用 visual studio 的輔助功能時的問題.
結論
如果就這兩個來比較, 使用 ConditionalAtrribute 取代 #if 會比較好, 如果因為 ConditionalAtrribute 的限制而無法使用, 最後再改用 #if.
不過這種需要依照環境切換邏輯的情境, 我會優先往 config 或後臺設定的方向思考, 除非用設定還是處理的不夠好, 才會往 ConditionalAtrribute 的方向想.
參考
C# : Conditional Attribute and #if Directive
If You’re Using “#if DEBUG”, You’re Doing it Wrong
#if (C# Reference)
Conditional (C# Programming Guide))
#if DEBUG vs. Conditional(“DEBUG”)